The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Visual Arts invites you to explore the vibrant world of creativity that shapes our culture and expressions. From the ancient strokes of painting to the innovative realms of digital art, visual arts have continuously evolved, reflecting society’s values and inspirations. This guide delves into the diverse techniques and forms of visual arts, highlighting their significance and the unique characteristics that set them apart.
Join us on this artistic journey as we uncover the rich history of visual arts, from traditional methods like watercolor and oil painting to the revolutionary impact of digital techniques and photography. Each section is designed to engage your senses and inspire your imagination, whether you are an aspiring artist, a seasoned creator, or simply an art enthusiast.
Overview of Visual Arts
Visual arts encompass a broad realm of artistic expression that is primarily visual in nature. They play a crucial role in culture, offering insights into the societal values, historical contexts, and emotional landscapes of various communities. Through paintings, sculptures, photography, and various forms of design, visual arts create a universal language that transcends barriers, fostering connection and understanding among diverse populations.
Their significance lies not only in their aesthetic appeal but also in their capacity to provoke thought, inspire movements, and reflect the human experience.The evolution of visual arts has been profound, tracing back to prehistoric times with cave paintings that served as the earliest forms of storytelling. Over centuries, visual arts have transformed through various movements and innovations, influenced by technological advancements and cultural shifts.
From the classical realism of the Renaissance to the abstract expressionism of the 20th century, visual arts have continuously adapted, mirroring the complexities of human existence. This dynamic evolution showcases the ongoing dialogue between tradition and innovation, enhancing the richness of artistic creation.
Characteristics of Visual Arts
Visual arts are distinguished from other art forms by several key characteristics that define their unique nature. These characteristics not only highlight the mediums used but also the intentions behind the artwork. Understanding these elements enriches the viewer’s experience and appreciation.
Medium Diversity
Visual arts include a wide array of forms such as painting, sculpture, photography, installation art, and digital media. Each medium carries its own potential for expression and interpretation.
Visual Communication
Unlike performing arts, visual arts rely solely on visual elements to convey messages and emotions. This visual language can evoke immediate responses, often bypassing verbal barriers.
Tangible Experience
Most visual artworks exist in a physical form, offering a tangible experience that allows for engagement through sight and touch. This aspect enables the viewer to interact with the piece on a personal level.
Cultural Reflection
Visual arts are deeply rooted in the culture from which they originate, often reflecting the values, beliefs, and historical narratives of a society. They serve as artifacts of cultural identity and heritage.
“Visual arts are the heartbeat of culture, echoing the stories of humanity through form and color.”
Recognizing these characteristics not only enhances our understanding of visual arts but also encourages a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of human creativity. Whether through a striking painting that captures the essence of emotion or a meticulously crafted sculpture that challenges our perceptions, visual arts continue to be a dynamic force in both personal and collective expression.
Painting Techniques
Painting is not just an art form; it’s a vibrant language that expresses emotions, tells stories, and captures the essence of life. With various techniques available, artists have numerous ways to translate their visions onto canvas. This segment delves into some of the most popular painting techniques, highlighting their unique qualities and potential applications in the world of visual arts.
Watercolor Painting, The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Visual Arts
Watercolor painting is celebrated for its translucence and fluidity. This technique utilizes water-soluble pigments that are activated with water, allowing for a range of effects from delicate washes to bold applications. Artists often work on wet paper to achieve beautiful blends and gradients, making it ideal for landscapes and portraits that require a soft touch. However, mastering watercolors requires skill and an understanding of the medium’s unpredictable nature.
Oil Painting
Oil painting boasts rich colors and a profound depth that artists have cherished for centuries. Utilizing pigments suspended in oil, this technique allows for slow drying times, giving artists the flexibility to manipulate their work over an extended period. Techniques such as glazing, impasto, and scumbling can create stunning textures and layers. The oil medium also permits extensive blending, making it a favorite for realism and intricate details.
Acrylic Painting
Acrylic painting is a modern marvel that combines the versatility of both watercolor and oil. Acrylics dry quickly and can be thinned with water or used straight from the tube for a more opaque finish. This adaptability allows artists to explore a wide range of styles, from rapid, expressive brushwork to detailed, layered compositions. The medium’s fast-drying nature makes it suitable for those who prefer to work quickly and experiment with techniques.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Techniques
The evolution of painting techniques reflects changes in artistic preferences and technological advancements. Traditional methods such as oil and watercolor have laid the groundwork for contemporary approaches, which often incorporate mixed media, digital elements, and innovative materials. The contrast between the meticulous methods of the past and the boundary-pushing styles of today showcases the dynamic nature of the art world.
Pros and Cons of Painting Techniques
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each painting technique can guide artists in selecting the right medium for their projects. Below is a comparative overview of watercolor, oil, and acrylic painting, highlighting their respective advantages and challenges.
| Technique | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Watercolor |
|
|
| Oil |
|
|
| Acrylic |
|
|
The choice of painting technique can profoundly impact the overall aesthetic and emotional resonance of a work of art.
Sculpture Forms
Sculpture is a three-dimensional art form that brings imagination to life through a variety of techniques and materials. From ancient times to the modern era, sculptures have represented cultures, emotions, and narratives. This exploration of sculpture forms provides insight into their diverse types, the materials that define them, and some of the most influential sculptors in history.
Types of Sculptures
Sculptures can be categorized into several distinct types, each with unique characteristics and artistic purposes. Understanding these forms enhances appreciation for the diverse expressions found within the world of sculptural art.
- Relief Sculpture: This form is carved into a flat surface, projecting from the background. It can be classified into high relief, where the figures stand out significantly, and low relief, where the projection is minimal. Notable examples include the Parthenon frieze in Athens, showcasing intricate depictions of mythology and history.
- Freestanding Sculpture: Also known as in-the-round sculptures, these pieces are designed to be viewed from all angles. They stand independently and can vary greatly in size and form. A classic example is Michelangelo’s “David,” which captures the human form in exquisite detail and is celebrated for its anatomical accuracy.
- Kinetic Sculpture: This innovative form incorporates movement, either through mechanical means or natural forces like wind and water. An iconic piece is Alexander Calder’s mobile sculptures, which gracefully change shape and position, engaging viewers with their dynamic nature.
Materials Used in Sculpture
The choice of materials in sculpture significantly influences the final artwork, affecting durability, texture, and aesthetic appeal. Different materials have been favored throughout history based on availability, technique, and the desired artistic expression.
- Stone: Marble, granite, and limestone have been traditional choices, valued for their durability and beauty. Michelangelo’s works often used Carrara marble due to its fine quality.
- Metal: Bronze and steel are commonly used for their strength and malleability. The lost-wax casting technique is frequently employed in bronze sculptures, allowing for intricate detailing.
- Wood: A versatile and warmer medium, wood has been used in sculptures across cultures, from totem poles to modern abstract forms. The natural texture adds depth to the artwork.
- Clay: This malleable medium is perfect for both sculpting and casting. It allows for fine details, and when fired, it becomes a durable ceramic. Artists like Henry Moore have famously utilized clay in their preliminary models.
- Mixed Media: Contemporary artists often combine various materials to create innovative sculptures that challenge traditional boundaries. This method allows for more personal expression and experimentation.
Famous Sculptors and Their Notable Works
The field of sculpture boasts numerous visionary artists who have left an indelible mark on the art world. Their unique styles and groundbreaking works continue to inspire new generations.
- Auguste Rodin: Known for “The Thinker” and “The Kiss,” Rodin revolutionized sculpture with his expressive forms and textures.
- Henry Moore: Renowned for his large-scale abstract sculptures, Moore’s works like “Reclining Figure” exemplify organic shapes and spaces.
- Louise Bourgeois: Her emotionally charged works, such as “Maman,” explore themes of femininity and family through innovative forms.
- Alberto Giacometti: Famous for his elongated figures, Giacometti’s “Walking Man” captures existential themes and the human condition.
- Antony Gormley: Known for installations like “The Angel of the North,” Gormley’s works often engage with the human body and its relationship to the environment.
Digital Arts
The digital arts realm has rapidly expanded, transforming the landscape of creativity and expression in the contemporary art world. From intricate digital paintings to awe-inspiring 3D models, this evolution has birthed a new generation of artists who are harnessing technology to revolutionize traditional forms of art.Digital art encompasses various forms, including digital painting, 3D modeling, and animation. The rise of this art form is attributed to technological advancements and the accessibility of powerful tools that empower artists to create without the limitations of physical media.
Artists can now experiment with an unprecedented range of colors, textures, and techniques, pushing the boundaries of imagination and creativity.
Key Software and Tools in Digital Art
The tools available for digital artistry are as diverse as the artists themselves. Below are some of the most widely used software and tools that facilitate the creation of stunning digital artworks:
- Adobe Photoshop: A staple in the digital art community, Photoshop offers a plethora of brushes and editing tools ideal for digital painting and photo manipulation.
- Corel Painter: Known for its realistic brush effects, this software mimics traditional painting techniques, making it a favorite among digital painters.
- Procreate: Available on the iPad, Procreate provides an intuitive interface and powerful capabilities for sketching and painting on the go.
- Blender: An open-source 3D modeling tool that allows artists to create stunning animations and visual effects, catering to both novice and professional users.
- Autodesk Maya: A leading 3D software used for animation, modeling, simulation, and rendering, popular in film and game development.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Art Techniques
Understanding the differences between traditional and digital art techniques is crucial for aspiring artists. The following table provides a clear comparison of key aspects related to both mediums:
| Aspect | Traditional Art | Digital Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials (paints, canvas, clay) | Software and digital tools (tablets, computers) |
| Ease of Revisions | Challenging to revise without starting over | Easy to undo and modify elements |
| Texture | Varied textures based on materials used | Can simulate various textures digitally |
| Cost | Can be expensive due to materials | Initial software cost, but less ongoing expense |
| Accessibility | Requires physical space and materials | Accessible anywhere with a digital device |
Digital art allows for limitless creativity and innovation, reshaping the future of artistic expression.
Photography as Visual Art
Photography has emerged as a pivotal form of visual art, evolving dramatically since its inception in the early 19th century. It has transitioned from a mere mechanism for capturing reality to a profound medium of artistic expression that challenges perceptions and conveys complex emotions. In contemporary art, photography stands alongside traditional mediums, inviting audiences to explore narratives, concepts, and the essence of the human experience through the lens of a camera.The evolution of photography has seen it become a versatile art form, giving rise to various styles that cater to different subjects and sentiments.
Understanding these styles is crucial for both artists and enthusiasts alike, as each approach offers unique perspectives and techniques that contribute to the visual arts landscape.
Photography Styles
Various photography styles serve distinct artistic purposes, each with its own characteristics. Here are some of the most recognized styles:
- Portrait Photography: This style focuses on capturing the personality and mood of individuals or groups. It often emphasizes facial expressions and poses, inviting viewers to connect with the subjects on a personal level.
- Landscape Photography: Landscapes are the primary subjects in this style, showcasing the beauty of nature. The composition, lighting, and time of day significantly influence the visual storytelling in landscape photography.
- Abstract Photography: This style moves away from traditional representation, focusing instead on shapes, colors, and patterns to evoke emotions or ideas. Abstract photography challenges viewers to interpret images beyond their surface appearance.
Analyzing a photograph’s composition and techniques involves understanding several fundamental elements. Each photograph is a carefully curated blend of various components that contribute to its impact.
Analyzing Composition and Technique
When analyzing a photograph, it’s essential to consider its composition and the techniques employed by the photographer. Key aspects include:
- Rule of Thirds: This compositional guideline suggests dividing the frame into a 3×3 grid to create balance and interest by placing focal points along the intersecting lines.
- Leading Lines: Photographers often use natural lines within a scene to guide the viewer’s eye towards the subject or to create depth in the image.
- Framing: This technique involves using elements within a scene to frame the main subject, drawing attention and creating context.
- Lighting: The quality, direction, and color of light can drastically change the mood and clarity of a photograph, influencing how the subject is perceived.
- Depth of Field: This refers to the range of distance that appears in focus. A shallow depth of field can isolate the subject from the background, while a greater depth of field can provide context and detail.
Understanding these elements allows viewers and aspiring photographers alike to appreciate the artistry behind each image, enhancing their overall experience with photography as a visual art form.
Graphic Design Elements
Graphic design is a dynamic field that combines art and technology to communicate ideas visually. It plays a crucial role in how information is conveyed across various media, making it an essential component of visual arts. By effectively utilizing design principles, graphic designers create compelling visuals that capture attention and deliver messages with clarity.Graphic design is underpinned by several key principles that enhance visual communication.
These principles include balance, contrast, emphasis, movement, pattern, repetition, and alignment. Understanding and applying these principles allows designers to create harmonious and engaging compositions that resonate with their target audience. The importance of these principles cannot be overstated; they guide the creation of effective designs that not only attract attention but also foster understanding and emotional responses.
Design Software for Graphic Designers
An array of design software is available, each offering unique features that cater to different aspects of graphic design. Familiarity with these tools is vital for any graphic designer to effectively bring their ideas to life. Below is a list of popular design software and a brief overview of their unique characteristics:
- Adobe Photoshop: Renowned for photo editing and manipulation, Photoshop provides tools for creating intricate designs, illustrations, and textures.
- Adobe Illustrator: Ideal for vector graphics, Illustrator is favored for logo creation, typography, and scalable artwork, allowing for high-resolution outputs without loss of quality.
- CorelDRAW: This versatile software is popular among illustrators for its powerful vector graphic capabilities and user-friendly interface.
- Canva: A web-based tool that simplifies design processes, Canva is perfect for quick graphic creation with drag-and-drop features and a vast library of templates.
- Sketch: Primarily used for web and mobile interface design, Sketch offers robust features for collaborative projects and prototyping.
- Adobe InDesign: This software excels in layout design and is extensively used for creating print media, such as magazines, brochures, and e-books.
Understanding essential graphic design terminology is crucial to mastering the craft. The following terms represent the foundation of graphic design concepts that every designer should know:
- Typography: The art of arranging type in a visually appealing manner to enhance the readability and aesthetic of the design.
- Color Theory: The study of how colors interact and influence perception, forming a basis for effective color choices in design.
- Hierarchy: The arrangement of elements in a design to guide the viewer’s attention and convey importance.
- White Space: The empty space around design elements that helps to create balance and focus, preventing clutter.
- Grid System: A framework used to organize content and maintain consistency throughout a design, enhancing visual coherence.
- Branding: The process of creating a unique identity for a product or company, including logos, colors, and typography that represent its values.
Understanding these graphic design elements and software tools empowers designers to create impactful visuals that effectively communicate their intended messages.
Installation Art
Installation art represents a dynamic and transformative genre within the visual arts, where artists create immersive environments that invite viewers to engage on multiple sensory levels. Unlike traditional artworks, installation art prioritizes the experience of space and interaction, often utilizing entire rooms or outdoor landscapes to evoke emotional responses and challenge perceptions.This art form blends various media, including sculpture, video, sound, and even performance, to create a comprehensive experience.
Installation art can range from small, intimate spaces to vast, sprawling exhibits, often tailored to the specific context of the location. The essence of installation art lies in its ability to immerse the viewer, transforming their understanding of the space and the artwork itself.
Famous Installation Artists and Influential Works
Many artists have made significant contributions to the field of installation art, pushing boundaries and redefining artistic expression. Here are some of the most notable figures and their influential works:
- Christo and Jeanne-Claude: Renowned for their large-scale environmental works, such as “The Gates” in Central Park, this duo enveloped the landscape in vibrant orange fabric, creating an unforgettable visual impact.
- Yayoi Kusama: Her immersive Infinity Mirror Rooms, filled with reflective surfaces and polka dots, offer a mesmerizing experience that explores themes of infinity and self-obliteration.
- Olafur Eliasson: Known for works like “The Weather Project” at the Tate Modern, Eliasson utilizes light, water, and air to create environments that challenge perceptions of nature and the self.
- Damien Hirst: Hirst’s “The Physical Impossibility of Death in the Mind of Someone Living” features a preserved shark in formaldehyde, provoking discussions on mortality and the nature of existence.
- Ann Hamilton: Hamilton’s installations, such as “the event of a thread,” combine text, sound, and textile to create experiential artworks that frequently engage audiences on an intellectual and emotional level.
Materials and Processes in Installation Art
The creation of impactful installations involves a diverse array of materials and sophisticated processes that bring the artist’s vision to life. Artists often choose materials based on the desired impact and the specific context of their installation. Common materials used include:
- Natural elements: Wood, stone, and plants can establish a connection with the environment, emphasizing themes of nature and sustainability.
- Found objects: Everyday items transform into art when recontextualized; artists often incorporate discarded materials to comment on consumerism and waste.
- Digital technology: Projections, interactive screens, and sound installations engage viewers in novel ways, blurring the lines between the physical and the digital.
- Textiles: Fabric can create tactile experiences, inviting viewers to touch and interact, as seen in installations using draped materials or soft sculptures.
The processes involved in crafting installation art are as varied as the materials used. Artists often experiment with site-specific elements, considering architecture and the surrounding space during the development phase. Collaborative efforts with engineers, architects, and other specialists are common to ensure that the final installation resonates with its intended message and audience experience.
“Installation art is not merely about the objects in the space; it’s about the space itself and how the viewer interacts with it.”
Mixed Media and Collage: The Ultimate Guide To Different Types Of Visual Arts
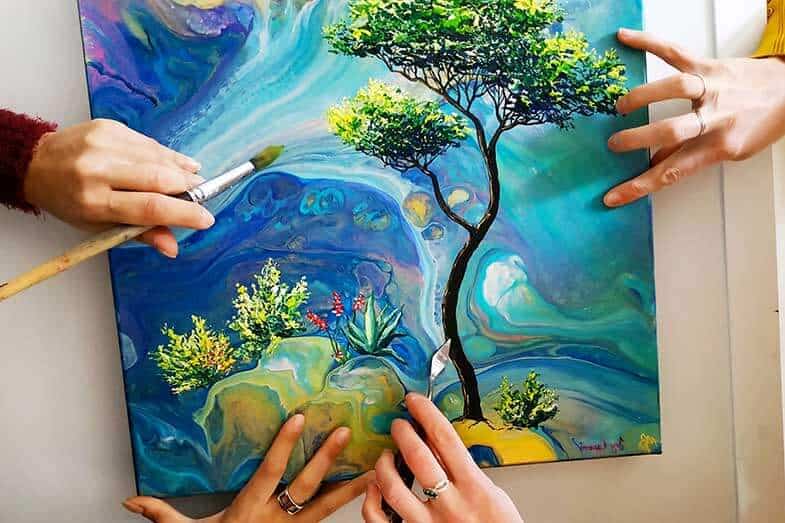

Mixed media and collage represent a vibrant fusion of artistic techniques, allowing creators to experiment beyond traditional boundaries. These methods encourage artists to combine various materials and mediums, reflecting the complexity of contemporary life. The significance of mixed media in modern art lies in its ability to challenge the viewer’s perception and engage them in a dialogue about the nature of art itself.Mixed media artworks involve the use of multiple materials—such as paint, fabric, paper, and found objects—allowing for a rich texture and depth that single medium works may lack.
Artists use these techniques to convey a narrative or evoke emotion, embodying the chaotic and multifaceted nature of modern existence. Collage, a subset of mixed media, is particularly notable for its innovative approach to composition, merging different visual elements to create a cohesive piece.
Techniques for Creating Mixed Media Artworks
Creating mixed media artworks involves a variety of techniques that encourage individuality and creativity. Here are some essential methods that artists often utilize:
- Layering: Building layers with different materials creates depth and complexity in the artwork.
- Texturing: Incorporating materials like sand, fabric, or paper adds tactile elements that enhance the visual experience.
- Found Objects: Using everyday items or discarded materials can imbue the work with a sense of history and personal connection.
- Painting Over Collage: Applying paint over a collage can unify the disparate elements and alter the overall aesthetic.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Creating a Collage Piece
Creating a collage can be straightforward yet creatively fulfilling. Here’s a step-by-step guide that illustrates the process:
- Gather Materials: Collect a variety of papers, magazines, photographs, and other materials that inspire you.
- Choose a Theme: Decide on a central theme or concept that will guide your collage.
- Cut and Arrange: Cut out selected images or materials and arrange them on your chosen base, experimenting with placement and composition.
- Adhere Elements: Use glue or medium to secure the pieces, layering them as desired.
- Add Finishing Touches: Enhance the collage with paint, markers, or other embellishments to unify the piece and add depth.
Artists Known for Their Mixed Media Works
Several artists are renowned for their unique mixed media styles, each contributing to the genre in significant ways. Their works are characterized by innovative techniques and profound thematic explorations, showcasing the potential of mixed media art. Here are a few influential figures:
- Robert Rauschenberg: Known for his “Combines,” Rauschenberg seamlessly integrated painting and sculpture using everyday objects and vibrant colors, breaking traditional art boundaries.
- Louise Nevelson: Nevelson’s monumental sculptures, often made from found wood and painted monochromatically, created immersive environments that invite viewers to explore dimensionality and form.
- Kara Walker: Through her cut-paper silhouettes that confront themes of race and identity, Walker employs mixed media to provoke thought and dialogue on social issues.
- Julie Mehretu: Mehretu’s large-scale paintings combine elements of architecture, cartography, and abstract forms, reflecting globalization and cultural intersections.
Performance Art
Performance art represents a unique fusion of visual arts and live action, where the body of the artist becomes a medium for artistic expression. This art form pushes boundaries beyond traditional visual representations, engaging audiences in real-time experiences that provoke thought and emotional responses. Unlike static artworks, performance art often reflects the artist’s personal narratives and societal issues, creating a dynamic dialogue between the performer and the audience.The effectiveness of a performance art piece can often hinge on several critical elements.
These include the artist’s physical presence, the use of space, the integration of time, and the emotional resonance of the work. Each of these elements contributes to the overall impact of the performance, transforming it into a memorable experience for viewers. The artist’s intention, the chosen setting, and the interactive nature of the performance can also significantly shape audience perception and engagement.
Elements of Effective Performance Art
To comprehend what makes a performance art piece resonate, it’s essential to explore the following elements that play a key role in its execution:
- Physicality: The artist’s movements, gestures, and expressions serve as a language that communicates deeper meanings.
- Space: The location of the performance can invoke specific contexts, enhancing or challenging the artwork’s themes.
- Time: Duration and timing can create tension, urgency, or reflection, adding layers to the audience’s experience.
- Audience Interaction: Engaging the audience can transform them from passive observers into active participants, deepening the impact.
- Emotion: The ability to evoke feelings is crucial; whether through humor, sorrow, or introspection, emotion can leave a lasting impression.
To better understand the distinctions between performance art and traditional art forms, the following comparative table highlights key features of each:
| Aspect | Performance Art | Traditional Art Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Live performance, often involving the artist’s body | Static mediums such as painting, sculpture, and photography |
| Interactivity | Often involves audience participation | Typically a one-way engagement from the viewer |
| Duration | Time-based; can vary greatly | Static; exists as a permanent object |
| Intention | Explores immediate, often personal or social themes | Can express broader or historical narratives |
| Experience | Ephemeral and unique to each performance | Consistent across viewings, often reproducible |
“Performance art is not just an art form; it is a dialogue that transforms the audience into co-creators of meaning.”
FAQ
What are visual arts?
Visual arts encompass a variety of forms of art that are primarily visual in nature, including painting, sculpture, photography, and digital art.
How can I start learning about different art techniques?
Begin by exploring online resources, taking classes, and practicing various techniques to find what resonates with you the most.
What is the difference between traditional and digital art?
Traditional art involves physical materials and techniques, while digital art is created using digital tools and software, offering unique creative possibilities.
Who are some famous visual artists I should know?
Notable artists include Pablo Picasso, Vincent van Gogh, Frida Kahlo, and contemporary digital artists like Beeple.
How do I analyze a piece of visual art?
Consider elements such as composition, color, technique, and the emotional response it evokes to understand its impact and meaning.